KMAG (KPLO MAGnetometer) is one of payload for KPLO and observes the
magnetic field around the moon. It was developed by Kyung Hee
University. The magnetic field of the moon exists only locally on
its surface, and this is called a magnetic anomaly. The origin of
this magnetic anomaly is still an unsolved mystery in the solar
system, and KMAG performs observations to solve the origin of the
magnetic anomaly on the moon.
The magnetometer was
developed using domestic technology in South Korea. The instrument
consists of a sensor unit with a boom structure and an E-box,
weighing about 3.5 kg. The sensor unit consists of a 1.2 m boom and
deployment structure, and three sensors that measure magnetic fields
with a resolution of 0.2 nT and a sampling rate of 10 Hz are
inserted into the boom.
The reason for using the boom
structure in the magnetometer is to minimize the magnetic field
interference generated by the satellite. The folded boom is deployed
to 135 degrees at the early operation of the mission. The three
magnetic sensors mounted on a boom can compensate for the
satellite's magnetic interference by discriminating it through a
multi-sensing technique.
After the launch, KMAG
successfully deployed its boom and it was the first to begin
observations among scientific payloads of KPLO. KMAG keeps
collecting scientific data during the whole KPLO mission. KMAG’s
observaional data will be used for research on the lunar magnetic
field and space environment.
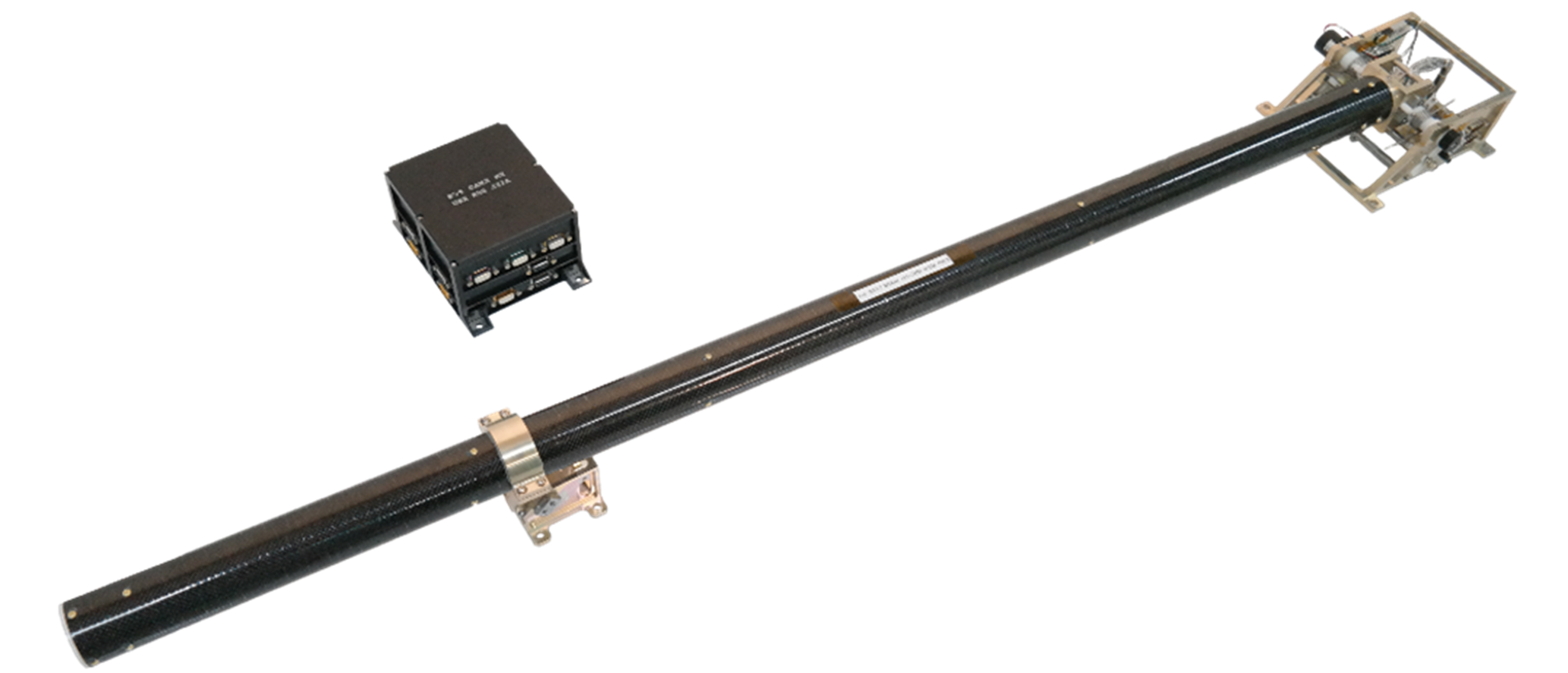 KMAG (Credit: KARI/KHU)
KMAG (Credit: KARI/KHU)
